If you're interested in orthopedics you won't want to miss this review! or fracture...
Scaphoid fractures account for 2-7% of all fractures and 50-80% of carpal bone fractures. The typical mechanism of injury is a FOOSH (fall on an outstretched hand).
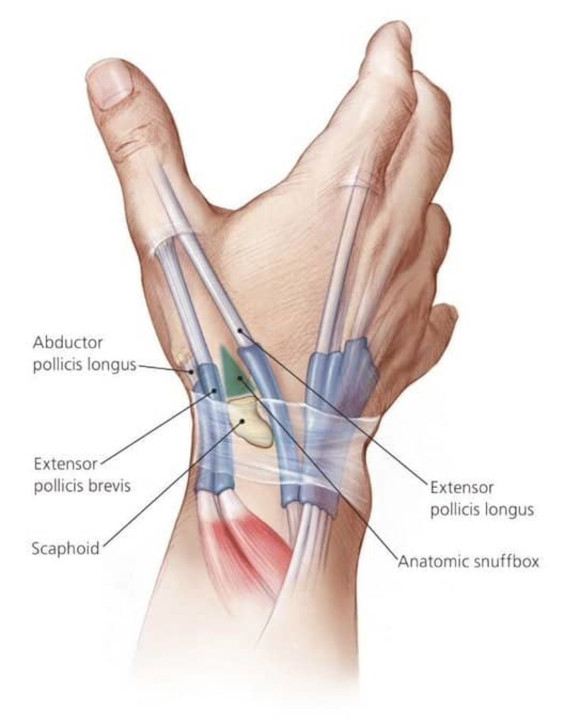
The anatomical snuffbox is made up of three tendons: the EPL, EPB, and ABL. The FPL is not a part of the anatomical snuffbox.
Patients with scaphoid fx may present with swelling, diminished grip strength, tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox or over the scaphoid tubercle.
The scaphoid has a retrograde blood supply with the dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery providing 80% of the blood supply while the volar arch providing 20%.
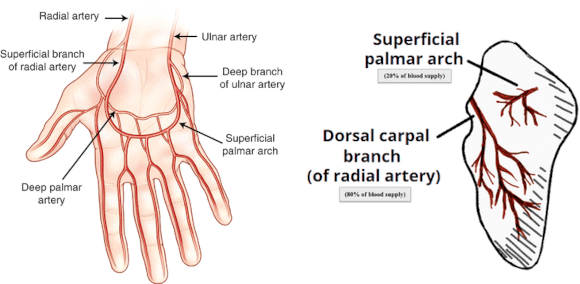
Due to the scaphoids’ retrograde vascular supply, the potential for AVN and non-union are concerning.
This fear is complicated by the fact that as high as 40% of scaphoid fractures are missed on initial presentation.
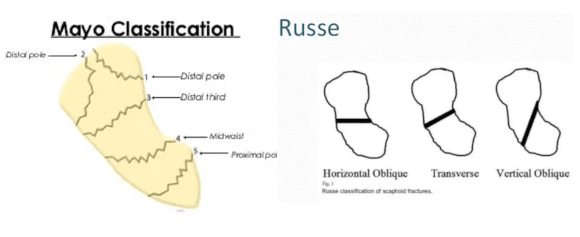
Fractures may be classified by their location (Mayo classification system) or by fracture pattern (Russe classification system)
The more proximal a fracture occurs the higher likelihood of AVN and non-union occurring.
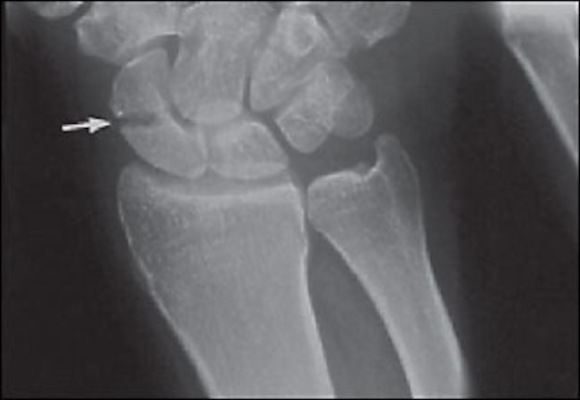
Scaphoid fractures may be missed with the use of conventional radiographs alone. Initial radiographs detect at most 75% of scaphoid fractures.
Radiographs may be repeated at a later date to aid in diagnosis.
MRI is the most sensitive test within 24 hours of injury.
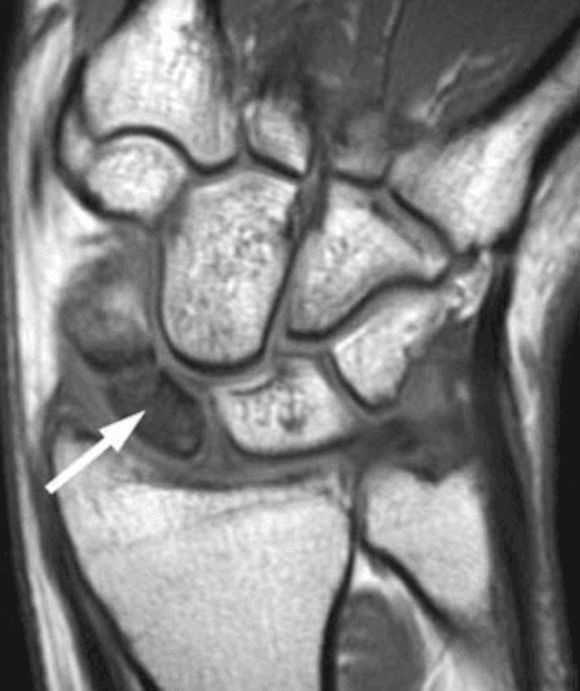
Scaphoid fractures with a displacement of <1 mm have a union rate of around 90%.
The prognosis is worsened with increased displacement, increasing fracture comminution, and if the fracture is initially missed.
Patients with non-displaced and stable fractures may be treated non-operatively with casting
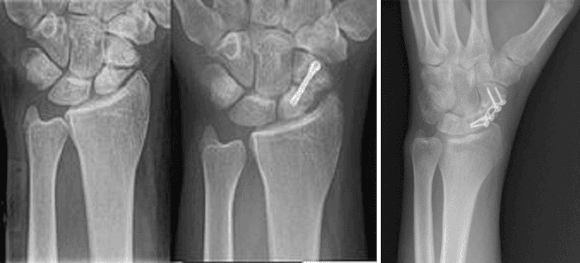
Fractures with displacement > 1 mm, angulation >10°, proximal pole fx, and comminuted fractures may be treated with ORIF either percutaneous screw fixation (left) or plate/screws (right)
Conclusion:
Due to the low sensitivity of initial radiographs in diagnosing scaphoid fractures physicians must be vigilant not to let this injury go undetected due to the risk of non-union and AVN.