An in-depth review of pediatric femoral shaft fractures.
If you're interested in orthopedics or pediatrics you'll definitely want to check this review out!
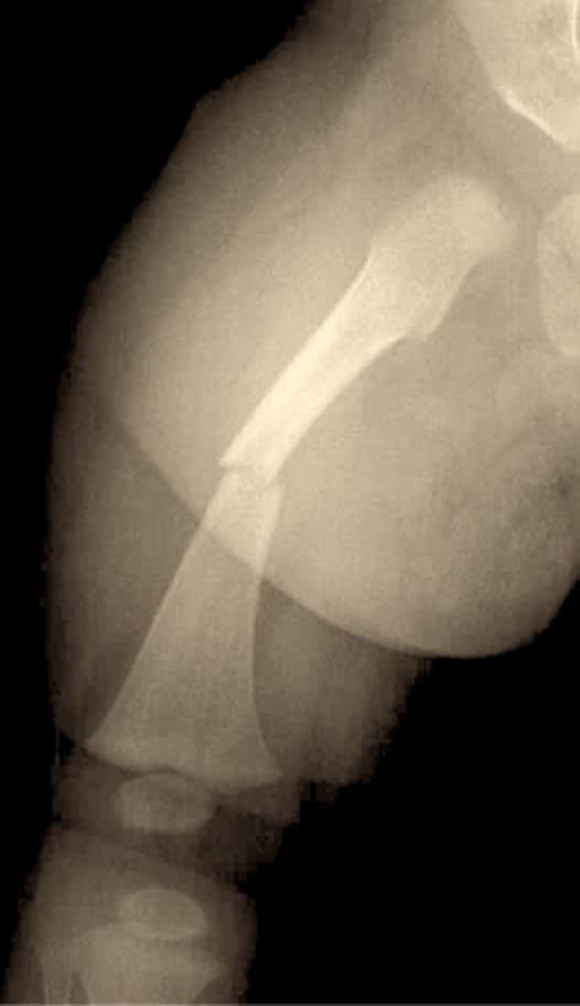
Pediatric femoral shaft (PFS) fractures constitute a small portion of pediatric fractures roughly 1-2% with a bimodal age distribution
Most common causes:
✯ Toddlers: falls
✯ Teenage/adolescent: MVA
In children younger than walking age child abuse must be suspected. As high as 80% of PFS fractures in this age group are due to child abuse.
In the toddler age group as high as 25% of PFS fractures are due to child abuse, so it must be ruled out.
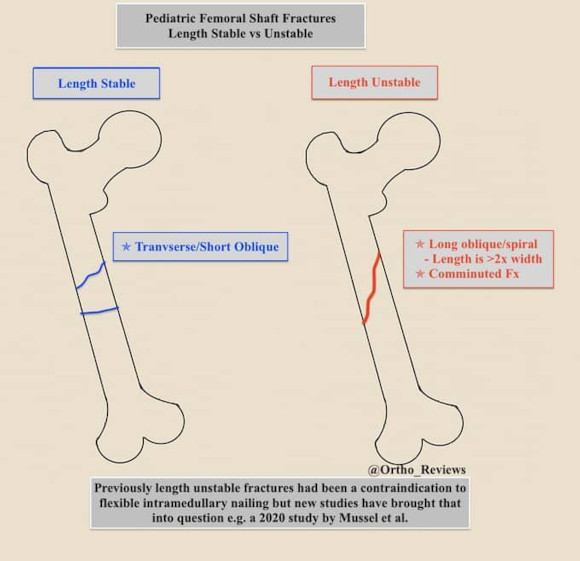
Length Unstable Fractures are described as:
✯ Long Oblique or Spiral Fractures
-Fracture length is > 2x the width
✯ Comminuted Fractures
✯ Commonly they have > 2 cm shortening
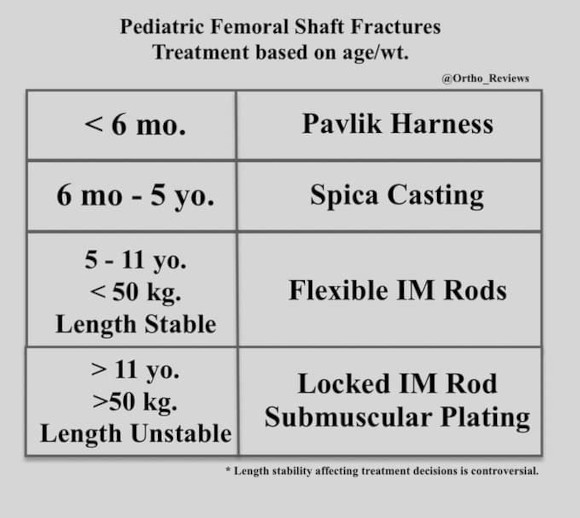
Treat options based on age, weight, and stability of fracture:
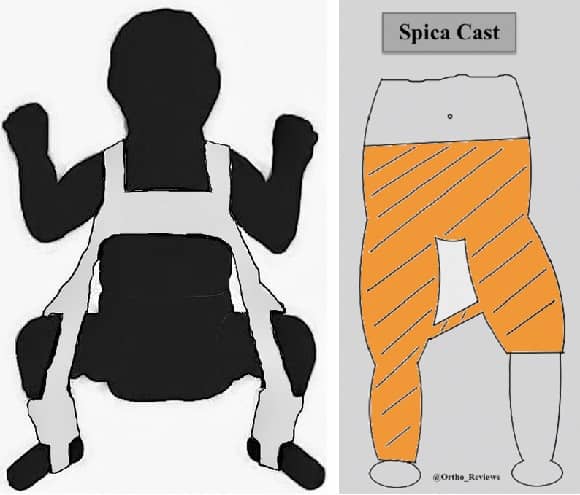
Non-operative management:
Children < 6 mo: Pavlik Harness (left)
Children 6 mo-5 yo: Spica Casting (right)
Acceptable reduction criteria for casting:
Sagittal angulation: 20°
Coronal angulation: 10°
Malrotation: 10°
Shortening: 2 cm
Operative management:
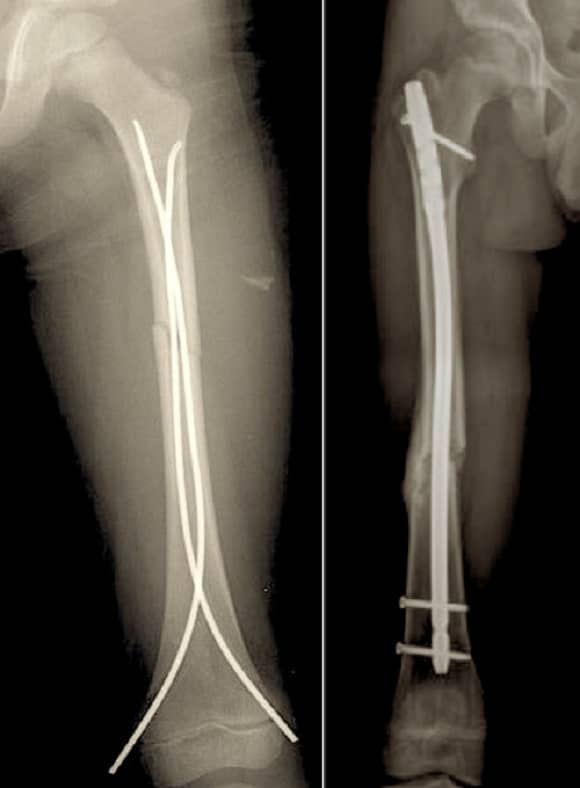
Flexible Intramedullary nailing: (left)
< 11 yo.
< 50 kg
Length Stable Fx
Rigid IM nail (right) / plating:
> 11 yo.
> 50 kg
Length Unstable Fx
Complications:
✯ Leg length discrepancy
✯ Nonunion is rare
✯ Muscle Atrophy
✯ Femoral Head AVN
Lateral trochanteric entry has a ↓ risk of AVN when compared to piriformis entry for antegrade nailing.
Full Review and Conversation on X